The recent Heavy Reading research report, “Network Automation for Tier 2/3 Service Providers,” focuses on the role of network automation in the operations of service providers with under $1B annual revenue. The data, insights, and recommendations contained in the report are a gold mine for Tier 2 and 3 service providers looking to get the most out of automation.
The core challenge that smaller service providers face is the cost and complexity of adopting new automation tooling and integrating it with their existing ecosystem, along with additional challenges like staffing constraints. However, network automation success can “help communications service providers (CSPs) build and operate networks more efficiently and reliably at lower cost and with greater innovation than ever before.”
As the report outlines, Tier 1 service providers have larger budgets, which has enabled them to lead the way in automation investment. The question is how smaller CSPs can most successfully follow suit.
Understanding Where Tier 2/3 Service Providers Are Today
The central study upon which the report is based involved a comprehensive survey of 217 qualified respondents. Heavy Reading set clear parameters for their respondents, such as a $1B revenue ceiling and a requirement that respondents be directly involved in “deploying, managing, purchasing, or using network automation, engineering, management, operations, or assurance solutions.” The responses confirmed the claim that Tier 2/3 service providers have been slower to invest in automation than their larger counterparts. However, they also indicate that interest in automation is nonetheless very high.
Here is the current state of play for automation adoption among Tier 2/3 CSPs:
- 30% still perform most operations manually (e.g., CLI-based config, legacy tooling).
- 52% have partially automated at least some network management tasks.
- 12% have achieved programmatic workflow-based, closed-loop automation.
- And only 6% of respondents say they have a “fully autonomous, self-driving network automation” operating model.
With just 18% of Tier 2/3 CSPs engaging in higher-level automation, there is much room for growth. And that’s not news — 81% of the respondents agree that more network automation is needed to stay competitive, and 74% agree that an increase in network complexity should be matched with more network automation.
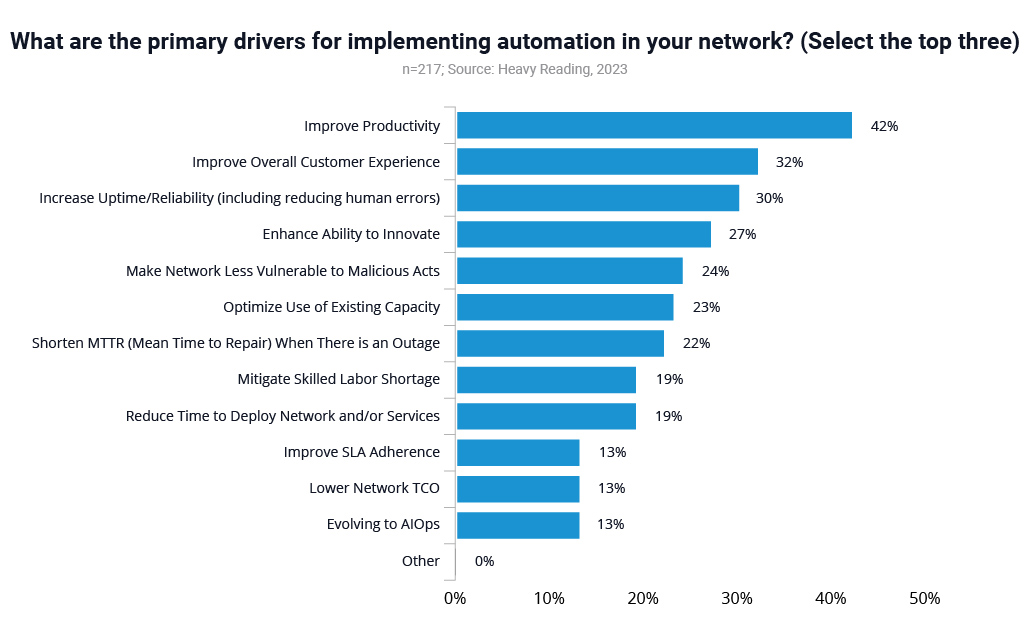
Further, when asked specifically about their own networks and the automation drivers they experience, several key areas came to light. The report states that “42% of respondents cited improving productivity, 32% picked improving overall customer experience, 30% named increasing uptime/reliability, and 27% chose enhancing ability to innovate — making these the top four drivers.”
Automation Challenges for Tier 2/3 CSPs
The factors that survey respondents cited as top challenges or blockers to more advanced automation include cost, complexity, and the difficulty of integrating automation tools with an existing ecosystem. These challenges are not unique to smaller CSPs, and the report states that larger Tier 1 CSPs tend to cite the same challenges.
But there is an additional group of challenges where the survey data between Tier 1 and Tier 2/3 CSPs differs more dramatically — those related to staffing constraints. Internal resistance to automation and fear of replacement is the #3 challenge reported in the Heavy Reading survey, while an insufficient number of staff is #4 and a lack of internal skills is #5.
To address the suite of challenges that could impact automation success, Tier 2 and Tier 3 CSPs must look to new, innovative automation solutions. Leveraging key developments in technology can help address and alleviate the challenges that a larger, higher-budget Tier 1 CSP might have simply been able to spend their way through.
Why Cloud-Delivered Network Automation Solutions Could Be the Answer
Using cloud delivery for network automation is an emerging approach that promises many benefits, but it is still relatively new. The level of endorsement for this new approach among survey respondents “one of the biggest surprises of the study.”
This surprise is in part because of the key concerns that most CSPs share around leveraging a public cloud environment for network automation applications and resources. Customer data storage, encryption, data sovereignty requirements, and SLA thresholds are significant considerations. However, despite these challenges, a staggering 93% of the Tier 2/3 CSPs surveyed for the report said they are “likely to adopt” SaaS-based network automation, with a full 26% stating they will “definitely” adopt the technology.
So why are Tier 2/3 service providers so enthusiastic? Simply put, cloud-delivered automation solves a lot of their most significant challenges:
Integration Complexity
SaaS-based automation solutions can help address the complexity of integrating automation tools, since they take an API-first approach to integration that enables fast, secure API calls from other applications. In addition, SaaS software is always up to date, and yet releases rarely affect APIs, ensuring that integrations are not impacted even as the software continues to improve.
Staffing Constraints
SaaS automation platforms are instantly accessible and do not require any staff to manage the infrastructure. In addition, these platforms tend to be designed for ease of use, with simple, modern, web-based GUIs that don’t require much training. Additionally, a SaaS automation solution enables a more dynamic, unified approach to storing information and automation assets. “The centralization of network automation data and workflows that reduce required expertise,” says the report, “allows better collaboration among network operators, engineers, field technicians, and other specialists.”
Release Agility
Two thirds of the Heavy Reading survey respondents indicated that they update automation software frequently. A cloud delivery approach “moves that burden from the operator to the software vendor.” As a result, automation can enable much more frequent updating, “which enhances the ability to innovate with new features faster.”
Implementation Speed
SaaS automation solutions can significantly accelerate automation implementations. The data from SaaS trials gathered by Juniper as part of the report indicated that, to fully set up an automation solution connected to devices, which might take months for a DIY project, took just a few hours. With 92% of respondents admitting that their DIY automation projects take longer than three months, the speed that SaaS solutions can offer is an important benefit.
Security
Public cloud environments deliver better security than most on-premises deployments due to built-in standards and capabilities. For example, the data centers used by Tier 1 cloud providers are ISO 27001 certified. In addition, “role-based access mechanisms and logging capabilities are typically more robust” than their on-premises counterparts, with a high degree of automation and damage control in place to respond to breaches or issues. And when it comes to vulnerability and patch management, cloud deployments enable organizations to be “more proactive than in on-premises deployments.”
Wrapping Up: The Business Case for Cloud-Delivered Network Automation
Cloud delivery comes with key technological advantages that answer the big challenges Tier 2/3 CSPs face when exploring automation adoption. When surveyed about the direct business case for automation, respondents ranked improvements to availability and reliability alongside large reductions in opex and TCO as the top benefits. In addition, cloud-delivered network automation eliminates a lot of complexity from integrating with the existing technology ecosystem and eliminates staff retraining needs.
The business outcomes are lower costs, faster service delivery, faster rollouts for new features and capabilities, and the ability to guarantee higher availability and resiliency by relying on the cloud’s built-in redundancy. Further, all of this comes with significant improvements to security. While traditional, on-premises automation software can be expensive and difficult to manage, only suited to the deep pockets of Tier 1 CSPs, the emerging SaaS network automation landscape meets smaller CSPs where they are. SaaS network automation can deliver all the benefits of automation while alleviating the potential pitfalls, making it a less risky, more promising path forward for Tier 2/3 service providers.