Share this
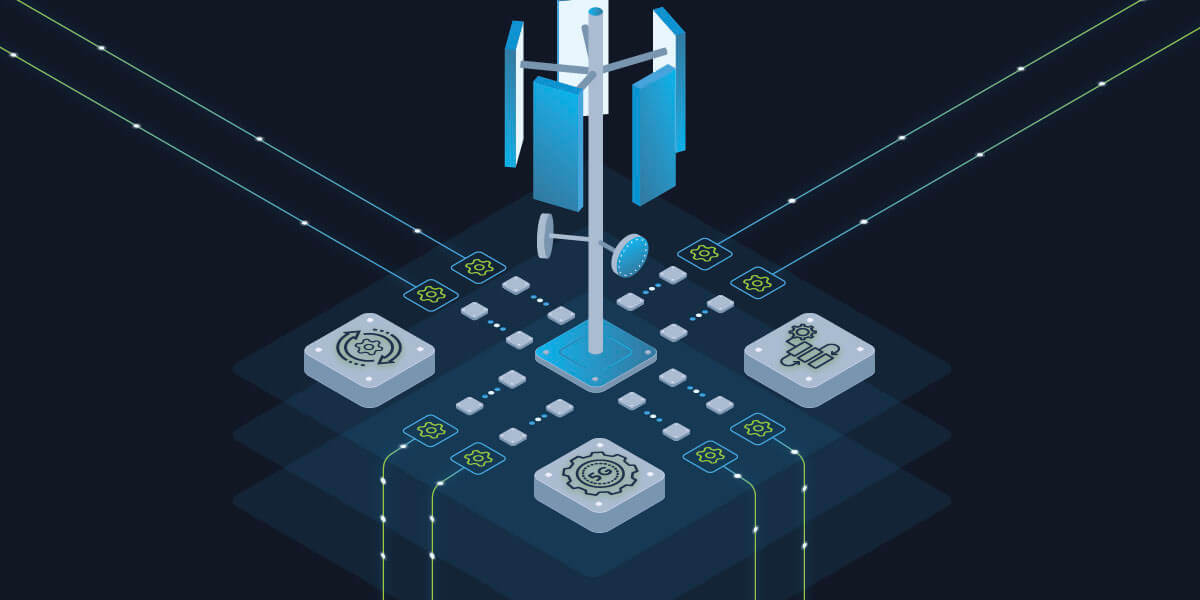

With the rush to 5G triggering an evolution of backhaul (cell site routers and aggregation routers), virtually every Communications Service Provider (CSP) is looking for ways to support this evolution through network automation. In my last blog, I covered the three essential components to look for when choosing an IP backhaul automation solution and today I want to focus on another very important topic to think about when building an IP backhaul automation strategy – the use cases.
Any good automation initiative starts by choosing the right use case. When it comes to IP backhaul automation, there are several key use cases that have emerged, and they all fall into three categories:

Implementation

Service Enablement
Operations
Let’s take a closer look at each category and the reasons it’s important to automate each.
Automating Implementation Use Cases to Support Capacity Changes
Implementation is one of the most common IP backhaul automation use cases. This includes the installation or configuration of new cell site routers or aggregation routers, capacity addition for activities like physical and bandwidth upgrades as well as circuit or traffic migration. These use cases can take advantage of capabilities like Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) to enable fully automated configuration of the new cell site routers or aggregation routers.
When automating implementation use cases, an automation platform is integrated with engineering databases and the DHCP environment to enable auto-detection of a new device, along with deployment of a Golden Configuration modified with device-specific variables provided by the engineering database.
With capacity additions and migration activities happening at greater frequency due to 5G rollouts, automating these activities is more important than ever – the provisioning of the cell site and aggregation routers to support the capacity change as well as coordination and orchestration between the IP device configuration changes, and the changes to the underlying transport such as the optical links or other physical layer changes.
Automating Operations Use Cases to Significantly Reduce Manual Effort
Next up, operations-based use cases include activities associated with the ongoing health and operation of an IP backhaul network, such as IP backhaul device upgrades, configuration compliance, device health checks, maintenance window automation, fault triage, and break-fix configuration activities.
By automating any of these activities, operations teams are able to perform significantly more activities with significantly less manual effort – enabling them to improve network reliability and performance in multiple ways:
- Improve Accuracy to Eliminate Outages: By replacing manual keyboard inputs with automated changes, accuracy improves dramatically and eliminates outages caused by incorrect input.
- Dramatically Decrease Health Check Time: By automating activities such as health checks and pre-post checks, operations team members can perform sophisticated checks in seconds instead of hours. This enables them not only to automate the checks that they were previously performing but perform more checks than would have been too time consuming in the manual method – improving accuracy and confidence that changes will not inadvertently cause disruption.
- Improved Data Management: All data associated with the execution of automated activities is saved to a database, which can be analyzed by machine learning systems to further improve quality and performance. Operations teams can begin to use this data to implement closed-loop automation use cases for triage and resolution of network errors.
Automating Service Enablement for Advanced 5G Functionality
Last up are 5G Service Enablement automation activities. These are related to configuration and implementation of IP backhaul devices to support, or improve support, for advanced 5G functionality such as 5G network slicing.
The backhaul network is a component of the Transport Network, which is one of the three network slicing domains in the 3GPP model (RAN, Mobile Core, and Transport Network (TN)). The TNs involvement in network slicing is primarily related to ensuring that the network can mee the technical requirements for each slice, particularly in the areas of the latency, bandwidth, and traffic isolation.
By leveraging an automation platform to support these activities, teams can expose more functionality to other orchestrators and controllers, enabling the network to deliver more responsively and offer higher value capabilities.
How Itential Supports IP Backhaul Automation Use Cases
The Itential Automation Platform is the perfect automator for any CSP to leverage for IP backhaul automation use cases. Itential now offers a packaged solution specifically for Cell Site Backhaul automation combining the Itential Automation Platform, along with pre-built and integrated components that are focused on automating these very use cases.
To learn more about The Itential Cell Site Backhaul Solution and how it can help your business automate a multitude of cell site backhaul use cases click here. You can also get a deep dive into backhaul automation as well as better understand the business impact and benefits of it in Itential’s “Accelerating 5G Evolution Through IP Backhaul Automation” white paper.





